This post was originally published on this site
Everyone “knows” that the U.S. government’s massive stimulus is the reason the U.S. stock market took off from its March 2020 lows. But, as Humphrey Neill, the father of contrarian analysis, constantly reminded his clients: “When everyone thinks alike, everyone is likely to be wrong.”
Conventional wisdom certainly appears to be based on the evidence. M2 money supply (consisting of cash, checking deposits, and so-called “near money” that can be converted into cash with little difficulty) has grown at a faster rate over the past 12 months than at any time over the last six decades. Sure enough, the S&P 500
SPX,
has turned in one of its strongest 12-month returns ever.
This is just one data point. To investigate whether it is the exception or the rule, I analyzed several decades of historical record in search of a statistically significant correlation between the Federal Reserve’s stimulus and the stock market. I came up empty. The bulls therefore need to think twice before reassuring themselves that the bull market will continue just because the Federal Reserve is committed to priming the monetary pump.
In searching for possible correlations, I relied on two different measures of the money supply. I focused on M2 Money Supply (cash, checking deposits, and so-called ‘near money’ that can be converted into cash with little difficulty) and the Federal Reserve’s total balance sheet assets (a broader measure which reflects the Fed’s direct intervention in the economy through the purchase of securities and Treasuries). Regardless of the definition, however, the correlations between the stock market and money supply are not stable over time.
On the one hand, over the last decade there has been a strong positive correlation, just as we’ve seen over the last 12 months and what the bulls are assuming is the general pattern. But, on the other hand, this correlation was negative before that, which meant that in those earlier years faster money supply growth was more often than not associated with slower stock market growth, and vice versa. That’s just the opposite of what the bulls are assuming.
After this first pass through the data, the most we can say is that sometimes faster money supply growth is good for stocks, and sometimes it isn’t.
That in turn suggests that the relationship between the money supply and the stock market is a lot more complex than most investors think. A full discussion of that relationship is beyond the scope of this column, but we know that it depends in large part on investors’ appetite for risk. In a “risk-on” environment, for example, it is more likely that aggressive Fed easing will be considered bullish. But when investors are preoccupied with the downside (“risk-off”) then an aggressive Fed might cause investors to become even more worried.
As is often the case, John Maynard Keynes, the famous British economist of a century ago, shrewdly captured this dynamic. He pointed out that central banks will be powerless to stimulate the economy if there is no appetite for risk-taking, and in such an environment the Fed’s efforts will be like “pushing on a string.”
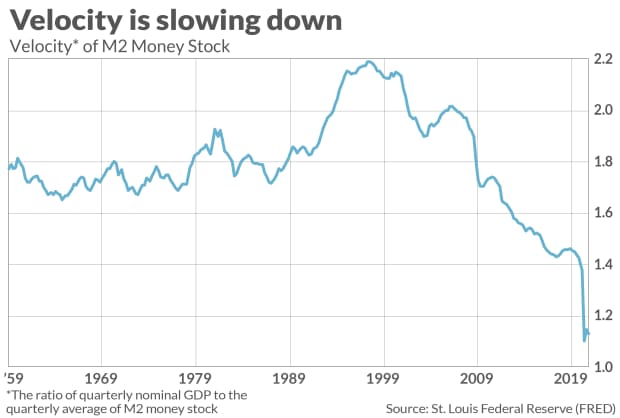
Another indication of the complexity of the relationship between money supply and the stock market is how much money velocity varies over time. I’m referring to the average number of times that money changes hands in a given year. When velocity declines, it takes a bigger money supply to have the same economic impact. Or, to put it another way, a bigger money supply won’t be stimulating if velocity declines too much in the process.
This puts recent experience in perspective. As you can see from the accompanying chart, velocity plunged at the beginning of the pandemic and remains at one of its lowest levels in six decades.
The bottom line: The money supply undoubtedly is related to the course of both the economy and the stock market. But its role is neither simple nor straightforward.
Mark Hulbert is a regular contributor to MarketWatch. His Hulbert Ratings tracks investment newsletters that pay a flat fee to be audited. He can be reached at mark@hulbertratings.com

